Alder Lake – What do we need to know?

Intel’s 12th Generation Core Architecture also known as Alder Lake brings with it a host of new features and considerations for those wishing to upgrade. For example, it brings a new socket and with it, considerations for cooling, DDR5 which has some interesting quirks when it comes to maximum supported speed on Alder Lake, PCIe 5.0, and some boards will feature 12VO. This means even power supply compatibility may be a factor!
Firstly let’s have a look at the lineup. It’s worth noting that the “F” variant omits integrated graphics but is identical otherwise. In the table below “P” or “P-Core” denotes performance core, and “E” or “E-Core” denotes an efficient core:
| Name | Cores | P-Core clocks | E-Core clocks | Base Power | Boost Power |
| i9-12900K i9-12900KF | 16 (8P + 8E) | 3.20 GHz base 5.10 GHz boost 5.20 GHz Max (TBM) | 2.40 GHz base 3.90 GHz boost | 125W | 241 W |
| i7-12700K i7-12700KF | 12 (8P + 4E) | 3.60 GHz base 4.90 GHz boost 5.00 GHz Max (TBM) | 2.70 GHz base 3.80 GHz boost | 125W | 190 W |
| i5-12600K i5-12600KF | 10 (6P + 4E) | 3.70 GHz base 4.90 GHz boost | 2.80 GHz base 3.60 GHz boost | 125W | 150 W |
Alder Lakes Performance cores offer hyperthreading so can service up to 2 threads simultaneously, Efficient cores lack HT so can only service one thread concurrently so an 8P +8E chip can service up to 24 concurrent threads.
TBM/max frequencies on 12900k/12700k relate to Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 which allows the CPU to boost beyond its normal boost frequency factors such as heat, power usage and workload allow it to do so safely.
Socket Compatibility
We probably all know this already but Alder Lake uses the LGA-1700 socket as opposed to the 10th/11th Gens LGA-1200 socket and as such will require a new motherboard to leverage one of these shiny new Intel CPU’s.
Cooler compatibility
LGA-1700 has a different stack height and as such is not directly compatible with LGA-1200/115x cooling systems however with that being said some manufacturers will offer mounting kits to adapt said coolers.
Even with a suitable mounting kit, it’s still advisable to check that your cooler is mechanically compatible with the motherboard as sometimes things like memory clearance or VRM heatsink clearance may cause an issue (and as such either additional effort to effectively cool the VRM’s/memory within clearance or a different motherboard/memory selection may be required). I know for a fact that some LGA-1700 boards have issues where VRM heatsinks will impede the installation of some popular heatsinks so I must stress the importance of checking this.
Some manufacturers offer great tools to help check the compatibility of their various coolers but most often you’ll need to check the manufacturers’ site and manually check mechanical compatibility with a particular board and cooler, many of these sites are not yet updated with specific motherboard compatibility but some such as Noctua’s are, I’ll attempt to update this as sites are updated however for the time being Noctua’s is the only one in the list:
There have been some early leaked photos of cooler contact issues however I think it best to wait and see concerning this point as details are scarce and it’s just as likely it was poorly installed or using early versions of mounting kits which may have since been improved.
Memory Compatibility
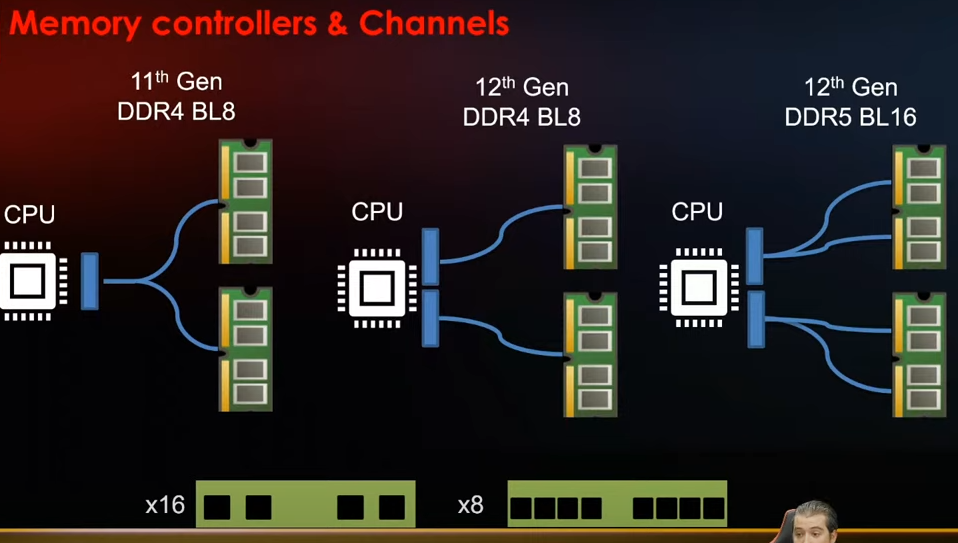
Alder Lake supports 2 channels of DDR4 or DDR5 and as such you need to make sure that you select/use the appropriate type of memory as despite having the same pin count and slot length, DDR5 is notched differently and as such will not fit in the same slot as DDR4. Whilst a DDR4/DDR5 combo board might be technically possible it’s highly unlikely that it would support both memory types simultaneously.
It’s also of course important to make sure that the heat-spreader on your memory has sufficient clearance for your CPU cooler. This is true of both DDR4 and DDR5 modules.
Memory Performance, reliability and support
I think it’s safe to say for most use cases DDR5 will be much faster, latency-sensitive workloads may be the only point that is a tad up in the air with lower end DDR5 vs high-end DDR4 however for most of us I think that is substantially offset by DDR5’s improvements, with that being said DDR5 on Alder Lake has some interesting caveats such as varying speeds depending on how many modules and what kinds of modules are installed.
The benefits of DDR5:
- DDR5 supports much higher clock rates (and hence greater bandwidth) up to 6400MT/s at current (Alder Lake supports at most 4800MT/s).
- Each DDR5 module has a pair of independent 32 bit data data busses as opposed to a single 64 bits data bus so can transfer data more efficiently.
- DDR5 burst chop length and burst lengths have doubled to 8 & 16 respectively which once again improves transfer efficiency.
Rambus has an excellent blog post if you’d like to have more of an in-depth read on DDR5.
Maximum DDR5 speeds:
Alder Lake officially supports “Up to DDR5 4800 MT/s” however that’s not the whole picture. The supported limit varies with the number of slots, how many modules are populated and how many memory ranks per module. These limits are the “non-OC” officially supported limits so they may or may not exceed them.
Assuming we’re always installing pairs of modules these are the maximum speeds that are supported by the CPU’s memory controller:
| Motherboard DDR5 Slot Count | Modules Populated | Rank(s) | Max. Frequency MT/s |
| 4 | 4 | 1 R | 4000 |
| 4 | 4 | 2 R | 3600 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 R or 2 R | 4400 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 R or 2 R | 4800 |
PCIe, and chipset features
Alder Lake and Intel 600 series chipsets bring with them PCIe 5.0 support which is very cool even if currently you’ll likely struggle to find many PCIe 5.0 devices to leverage the enormous amount of bandwidth these slots can provide. An interesting and potentially confusing thing when reading spec sheets for Alder Lake and its associated motherboards is that PCIe 5.0 is ONLY supported from the CPU and not the chipset and of course motherboard manufacturers will combine these capabilities in varied combinations so always check the motherboard spec sheet before purchase. I’ve noted this point as some sites mistakenly reported from leaks that it was not going to have PCIe 5.0 support.
As with all prior versions of PCIe both revisions 4.0 and 5.0 maintain full backwards compatibility so it should be fine from a bus perspective to pair Alder Lake with that old GTX 1080 TI or a brand new RTX 3090.
Alder Lake CPU’s Support the following:
| Interface | Count |
| PCIe 5.0 | Up to 20 lanes in 16+4 or 2×8 + 4 configurations |
The CPU communicates with the 600 series chipset via a DMI 4.0 lane which provides 8 lanes @ 16GT/s ea (the same speed as an 8x PCIe 4.0 link).
The Z690 chipset can provide the following ports:
| Interface | Count |
| PCIE 4.0 | Up to 28 lanes in 1x, 2x, 4x configurations |
| USB 3.2 2×2 (20Gb/s) | Up to 4 |
| USB 3.2 2×1 (10Gb/s) | Up to 10 |
| USB 3.2 1×1 (5Gb/s) | Up to 10 |
| USB 2.0 | Up to 14 |
| SATA 6Gbps | Up to 8 |
Power Supply and 12VO
Most motherboards will simply support the good old 24 pin ATX with the usual supplemental EPS 4 pin connectors as needed. However, there are also some 12VO motherboards being released by some manufacturers. This means you should double-check which connectors your power supply and motherboard has. 12VO adaptors do exist however it may be best to check with your PSU manufacturer or test the unit yourself. This is important as some units particularly older or lower quality PSUs will not remain in spec if they’re used with their other rails completely unloaded as 12VO only supplies 12v ;).
DRM Issues
If you’d like to see which games are known to be impacted by these issues Intel have published a list, they also have instructions for a work-around. Some motherboard manufacturers also have implemented their spin on fixes such as Gigabyte’s solution which parks the E-Cores on the fly. Their solution is comparable to Intel’s solution but automatically triggered as opposed to requiring a press of scroll-lock.
Update: as of 4th of December 2021 only 3 games remain on the list of affected titles:
- Assassin’s Creed: Valhalla
- Fernbus Simulator
- Madden 22